IntroVMware Edge Compute Stack
VMware Edge Cloud Compute Stack is a Solution for running workloads on the Edge - "Edge" in this case means running a modified Version of ESXi on really small compute footprint. Management is done from a central Appliane called VECO (VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator).
ECS vs VCF
ECS has nothing todo with VMware Cloud Foundation Edge (VCF-Edge). VCF Edge is just a SKU. VCF has different Edge Reference Architectures. ECS is a different Product, generally meat for smaller compute needs.
Management - Edge Cloud Orchestrator
Unlinke vSphere you won't deploy a vCenter to manage your ECS Hosts. In a classic vSphere Infrastructure the vCenter is Control- and Management Plane. In ECS your Management Plane is the VMware Edge Cloud Orchestrator (VECO). This Appliance runs either as a SaaS Service (on Google Cloud) or can be deployed on-premises.
Control Plane Components are always residing on the Edge Site, so you do not need constant connectivity to VECO.
Compute - ESC Hosts
ECS Hosts (a modified Version of ESXi, but with full ESXi Capabilities) can be even consumer Hardware with very small energy consumption. Like Barebones, NUCs, etc. You do not need beefy enterprise servers.
You can even have USB to RJ45 Network Adapters with the VMware USB Network Driver Fling!
Just follow the VMware VGC for supported Hardware.
Each ESC Host has to be booted from a custom ISO, which can be downloaded from VECO. The ISO is a little bit over 2GB in Size.
GitOps Approach
The unique thing about ECS is you manage the ECS Hosts and the Workloads with a GitOps approach. The configuration of the ECS Hosts like Networking, vSwitch Config is defined via yaml and stored in a Git Repository. The ECS Hosts has FluxCD installed on will check within the GitRepo for new yaml Manifests. FluxCD has a pull based approach - the destination (the ECS Host) will pull the config (yaml Files) themselves. With this approach it isn't a big Problem if the Edge Site does not have constant connectivity.
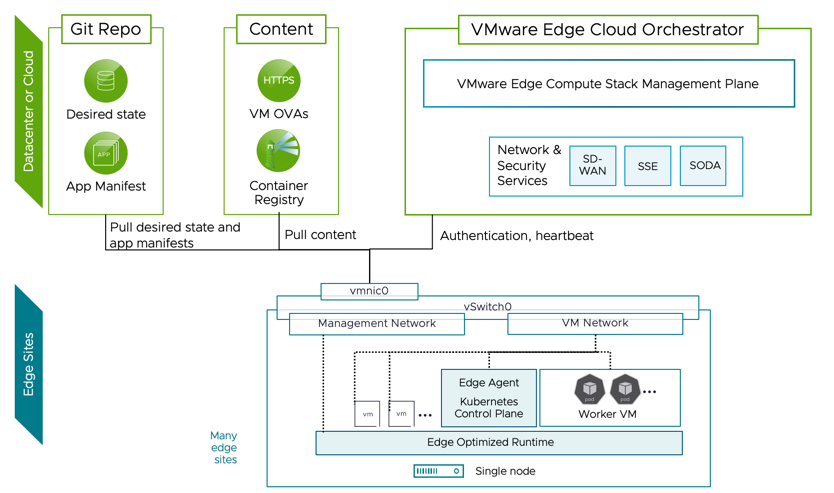
You cannot modify anything manually, the ECS Hosts will only have the GitRepo as a Configuration Source.
The ESC Hosts must have Network Connectivity to the desired GitRepo you add within VECO.
Example
#Example host configuration adding a new vSwitch and portgroup and assigning them to vmnic1
apiVersion: esx.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: HostConfiguration
metadata:
name: vswitch-config
namespace: esx-system
spec:
layertype: Incremental
profile: |
{
"esx": {
"network_vss": {
"switches": [
{
"name": "vSwitch1",
"policy": {
"nic_teaming": {
"policy": "LOADBALANCE_SRCID",
"notify_switches": true,
"rolling_order": false,
"link_criteria_beacon": "IGNORE",
"active_nics": [
"vmnic1"
],
"standby_nics": []
},
"security": {
"allow_promiscuous": false,
"mac_changes": false,
"forged_transmits": false
},
"traffic_shaping": {
"enabled": false
}
},
"bridge": {
"link_discovery_protocol": {
"protocol": "CDP",
"operation": "LISTEN"
},
"nics": [
"vmnic1"
]
},
"num_ports": 1024,
"mtu": 1500,
"port_groups": [
{
"name": "VM Network 16",
"vlan_id": 0
}
]
}
]
}
}
}
Workloads
Workloads on ECS can either be classical VMs or Kubernetes Workloads. For Kubernetes Workload a single Kubernetes Worker Node will be deployed on the ESC Host. ESC Kubernetes has nothing todo with Tanzu or vSphere Kubernetes Services. It's a much simpler approach with less footprint.
VM Deployment are done via Virtual Machine Classes (same approach as VMClasses in vSphere IaaS Controle Plane). You can either deploy Linux or Windows Workloads.
Windows Workloads are also deployed with yaml Manifest. You can even use sysprep or Powershell within the yaml. Thats quite a new way to deploy Windows!
Example:
apiVersion: vmoperator.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: VirtualMachine
metadata:
name: windows-server
namespace: default
spec:
className: best-effort-large
imageName: windows-server-2022.ova
powerState: poweredOn
networkInterfaces:
- network: workload-network
vmMetadata:
configMapName: windows-sysprep-config
transport: ExtraConfig
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: windows-sysprep-config
namespace: default
data:
userdata: |
#cloud-config
hostname: win-server
users:
- name: administrator
passwd: VMware1!
runcmd:
- powershell -Command "Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))"
- choco install -y googlechrome
Kubernetes
To deploy a Kubernetes Worker Node on the ESC Host use the following example yaml File:
# Example of how to change the default kubernetes worker node configuration to provide more memory or CPUs
apiVersion: vmoperator.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: VirtualMachineClass
metadata:
name: best-effort-ec-small
# No resource requests/reservations.
# Memory overcommit possible.
spec:
# VM operator controller name for VirtualMachine class
# is different so addition of controllerName attr with invalid
# value makes vm operator ignore this VM CRD instance.
# This is majorly done because vm operator doesn't have all the
# needed capabilities to deploy ec worker vm.
controllerName: vmoperator.vmware.com/ecworker
hardware:
cpus: 4
memory: 8Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ec-system
---
apiVersion: vmoperator.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: VirtualMachine
metadata:
name: ec-worker
namespace: ec-system
spec:
className: best-effort-ec-small
imageName: ec-wrkr.ova
powerState: poweredOff
vmMetadata:
transport: CloudInit
Note
After the worker virtual machine is created and booted, changes to desired state are not applied to it until the next Edge Compute Stack Host reboot.
Kubernetes Networking
Kubernetes Networking on the ESC Hosts is very simple. No need for Ingress Controllers. Workloads can be directly exposed with Nodeport.
Networking
LAN Connectivity will rely on vSwitches, NSX isn't designed for ECS as the footprint is too big. But for the WAN Connectivty, well there is a really good solution: VeloCloud SD-WAN
SD-WAN
VeloCloud SD-WAN can either be deployed as a Virtual Appliance or Hardware. VeloCloud allows for SD-WAN Connectivity, L3+L4+L7 Firewall and VPN Services as well as a lot of other features. VeloCloud SD-WAN deploys so called "Edges", the Appliance that will handle the traffic (Data Plane). The Management will be done from the SD-WAN Orchestrator Appliance, either running onpremises or as a SaaS (running on Google Cloud).
Clusters
As of now two topologies are supported in a Edge Site:
- One Node
- Two Node
I heard some rumors that three Nodes ESC Setup (event with vSAN) is comming ;)